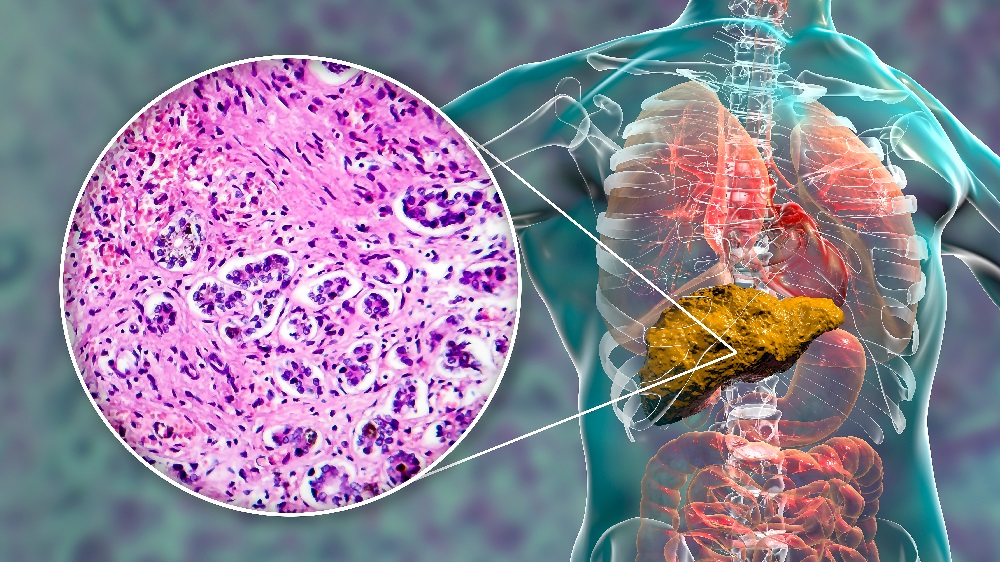

Hepatocellular Carcinoma is liver cancer that often results from chronic liver diseases such as cirrhosis caused by hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection. Early diagnosis and treatment enable the life of the liver through surgery or transplant. Depending on individual needs and liver conditions person has surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and target therapy as treatment options available. At the initial stage, it does not come with any symptoms. However, as the disease progresses, the person may experience bloating, weight loss, nausea, vomiting, feeling heaviness in the upper belly.
The exact cause of Hepatocellular Carcinoma is still a question to be answered. Yet experts consider some liver conditions that can trigger Hepatocellular Carcinoma. It includes anything that causes liver damage. Obesity and High sugar level are at the topmost as they can lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, which can progress into Hepatocellular Carcinoma.
Diagnosis needs experts to conduct a blood test. Experts check the ratio of AFP in blood. A high concentration of AFP in the blood can be a sign of liver cancer. Experts recommend Imaging tests like CT scans, Ultrasound, and X-rays to identify tumours in the liver. A liver biopsy allows experts to remove some cells from the liver and view them under a microscope for detecting the presence of cancer cells.
Deciding on the treatment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma needs a close and detailed discussion with experts. Surgical removal of the cancer cells and margins of healthy tissues is an option for the person with early-stage liver cancers. The person whose cancer has not spread beyond the liver can opt for liver transplant surgery. People who cannot undergo surgery can select ablation procedures to kill the cancer cells in the liver.