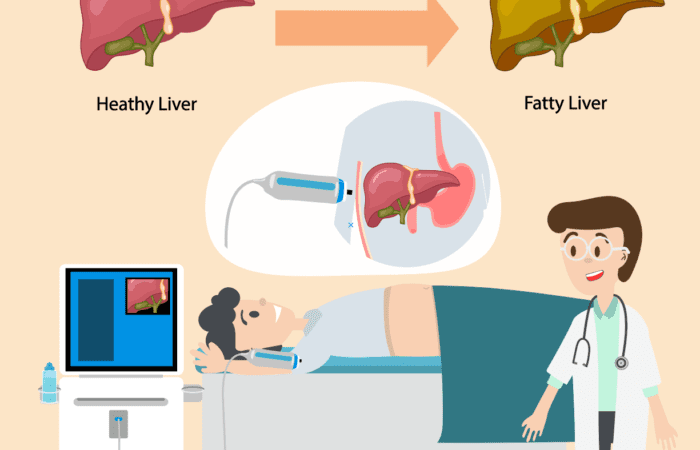

Fibroscan is a non-invasive method used to diagnose liver diseases like liver cirrhosis or scarring. It is an alternative to liver biopsy that facilitates the assessment of liver damage. The technique is also known as transient elastography and helps know the amount of fat in the liver. It works similarly to ultrasound involving the emission of a small pulse of energy, called a shear wave. The score shear waves produce helps to determine overall liver health.
Experts recommend fibroscan if they doubt the existence of persistent liver diseases like Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Alcoholic Liver Disease, or Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH). For a comprehensive evaluation of liver disease, experts may recommend diagnostic imaging and laboratory tests along with fibroscan.
The process needs the person to lie and relax on the medical table. The technician will ask the patient to place his right arm under his head, and then he places the FibroScan ultrasound wand over the upper right quadrant of the abdominal area, below the ribs. The instrument records a frequency produced when waves hit the organ. It is a comfortable process that takes a time of fifteen minutes.
The test uses a pointing scoring system to grade the degree of liver fibrosis. The five-pointing scoring system score determines the degree of liver fibrosis, from F0-F4. The normal score range is between 2 and 6 kPa anything beyond this range indicates the presence of liver disease.